Hello all,
In this topic, I will be talking about encryption and decryption using OpenSSL in PHP. I will be briefly discussing what “two way encryption” is and how to use it in your PHP application using OpenSSL encrypt and decrypt methods with a readily usable example. At the end of this page there will be a zip file where you can download and run the example.
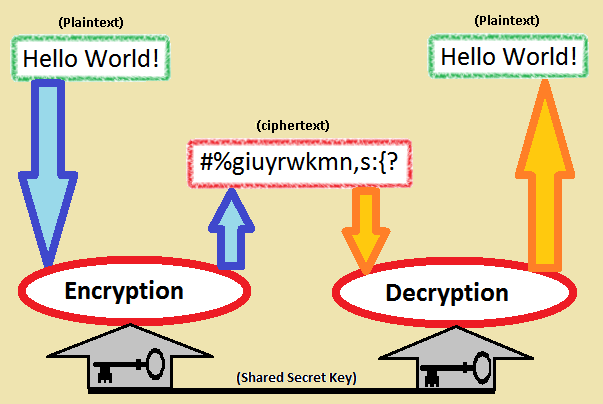
Two way encryption (encryption and decryption) is the simplest way of securely sending some sensitve information over the Internet using a shared secret key. To make things understandble picture this scenario. A web user fills a form with some data and press the submit button. When the form is submitted, data will go from place A to place B. If we send data as it is, anyone (i.e. Spy) has access to data packets can open and see what’s inside. So, before sending data as it is we will use a convertion method (encryption) to transform human readable data (i.e. Plain text) into a human unreadable format (i.e. Cipher text). Then the receiving end will perform a data convertion exercise (decryption) to transform data back to readable format.
(Image URL :- https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Crypto.png)
In PHP there is openssl_encrypt function available to encrypt a plain text using a hash key. Let’s take an example,
openssl_encrypt($textToEncrypt, $encryptionMethod, $secretKey, $options, $iv);
openssl_encrypt takes five parameters which are,
- $textToEncrypt – The plain text that needs to be encrypted
- $encryptionMethod – Encryption method (Using openssl_get_cipher_methods, available methods)
- $secretKey – A key (needs to kept private)
- $options –
OPENSSL_RAW_DATAorOPENSSL_ZERO_PADDING(Default is 0) - $iv – An initialisation vector. (precisely 16 bites)
The above will give you the encrypted text of the given plain text. When it comes to decryption you would only need to know the $secretKey and $iv which can be derived from the $secretKey (or can be unique on its own). The initialisation vector ($iv) is a random number which makes sure that the encrypted text is unique. It is important to learn about this $iv. (Refer to this link to learn more about $iv)
I have used the following to generate $iv,
$bytes = "";$last = "";
while(strlen($bytes) < 48) {
$last = md5($last . $secretHash, true);
$bytes.= $last;
}
$iv = substr($bytes, 32, 16);
To decrypt above created cipher text we can use openssl_decrypt function. Let’s see an example,
openssl_decrypt($cipherText, $encryptionMethod, $secretKey, 0, $iv);
openssl_decrypt takes five parameters which are,
- $cipherText – The encrypted text that needs to be decrypted
- $encryptionMethod – Encryption method (Using openssl_get_cipher_methods, available methods)
- $secretKey – A key (needs to kept private)
- $options –
OPENSSL_RAW_DATAorOPENSSL_ZERO_PADDING(Default is 0) - $iv – An initialisation vector. (precisely 16 bites)
Executing above will give you back the plain text data. The following link will contain two sample programs one to encrypt and one to decrypt. All you need to do is extract this inside your web directory (www or htdocs). Then visit “http://your_local_host/OpenSSL/encrypt.html” to bring the encryption form. Type anything you like that needs to be encrypted and press the submit button. In the follow up screen, copy the cipher text from the textarea. Next, visit “http://your_local_host/OpenSSL/decrypt.html” and paste the copied cipher text into the textarea and press the submit button. In the next screen you will see the plain text that you have typed earlier.
Click here to download the zip file.
I hope you enjoyed the post. Feel free to leave your suggestions, feedback in the comments section below. Thank you 🙂